Scope
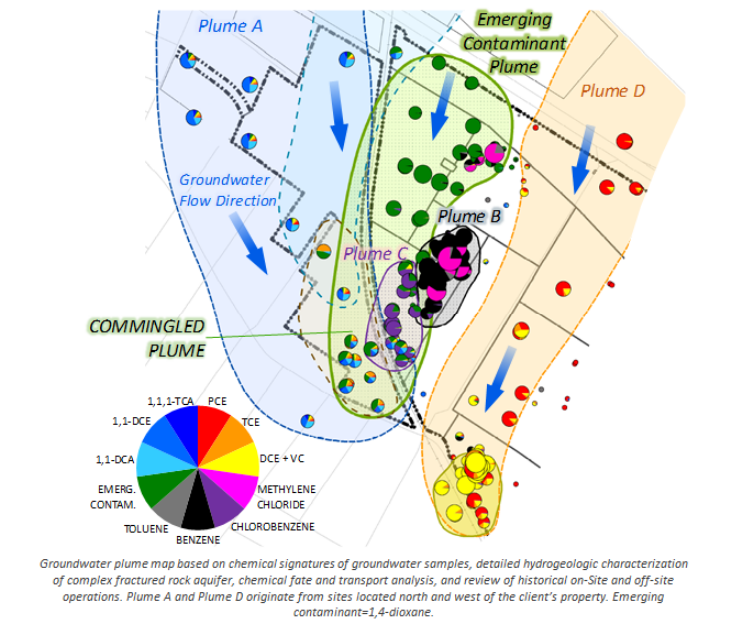
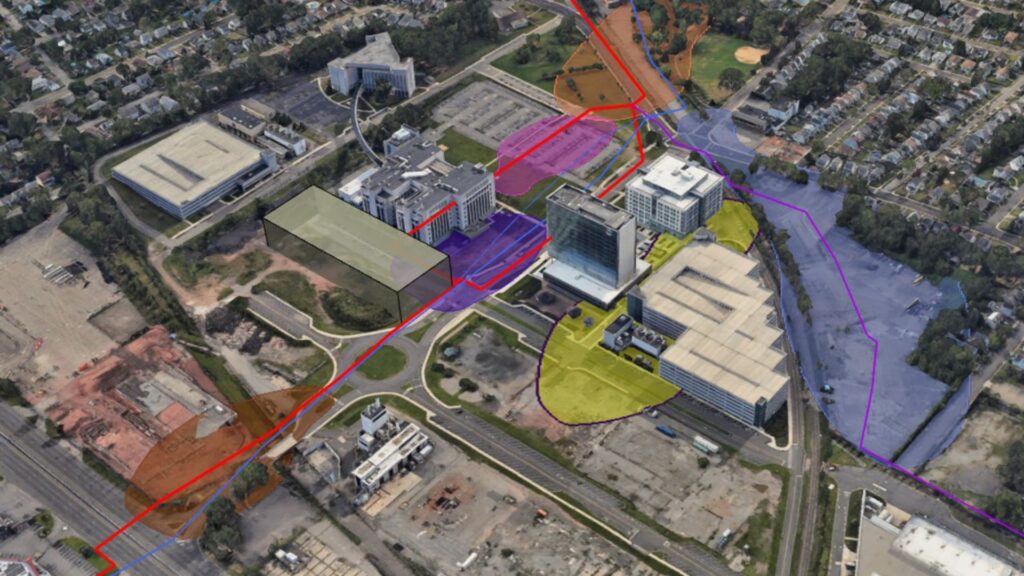
Investigation design and analysis of hydrogeologic data at complex fractured bedrock site enabled identification of PRPs responsible for groundwater plumes beneath and downgradient of manufacturing plant. Investigation findings provide a basis for remedial design and plume apportionment. Prepared a comprehensive Conceptual Site Model report for legal counsel.
Process
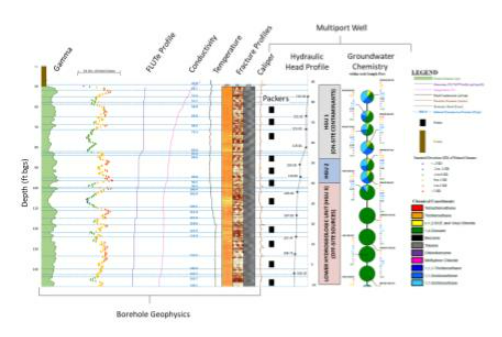
- Development of the CSM was based on integration of large dataset including chemical and hydraulic data from 1,100 wells (300 at depths 100-600 ft bgs), 19,800 soil samples from 9,000+ locations, multiport wells (19 to 24 ports/well), surface and borehole geophysics (110 borings), rock coring, and integration of on-site and off-site historical records. Bedrock aquifer is contaminated with DNAPL, VOCs, and 1,4-dioxane. The resulting conceptual site model includes multiple dipping hydrogeologic units (HGUs) offset by faults.
- Part of this work included development of a custom data analysis tool.
Chemicals in soil, rock, and groundwater included the following:
- 1,1,1-Trichloroethane (TCA)
- 1,1-Dichloroethylene (1,1-DCE)
- 1,2-Dichloroethylene (1,2-DCE)
- 1,1-Dichloroethane (1,1-DCA)
- Tetrachloroethylene (PCE)
- Trichloroethylene (TCE)
- Cis-1,2-Dichloroethylene (cis-1,2-DCE)
- Vinyl Chloride (VC)
- Chlorobenzenes (monochlorobenzene and 1,2-dichlorobenzene)
- Emerging Contaminant: 1,4-dioxane
- Benzene
- Toluene